Do you want to know ‘What is WordPress Gutenberg full site editing?’ If so, you’ve landed on the right page!
In July 2021, WordPress 5.8 first introduced Gutenberg full site editing with the template editor. The same year, by December, WordPress 5.9 came out with the “full shipping version,” offering a complete Gutenberg full site editing experience.
WordPress Gutenberg Full Site Editing (FSE) introduced tools for visual editing and user-friendly editing. It makes working on different parts of your WordPress website easier. With FSE, you can easily adjust your website’s design and layout using a graphic interface, making WordPress feel like a user-friendly page builder.
In this WordPress Gutenberg tutorial, we will explain everything you need to know about WordPress Gutenberg full site editing and show you how to use it to make changes to your site.
Ready? Let’s get started!
What is WordPress Gutenberg Full Site Editing?
Gutenberg Full site editing (FSE) is a term you’ll hear often in the WordPress community. It’s not just a single feature. Instead, it refers to a collection of powerful new features in Gutenberg. These features make a huge difference in how you build and customize your WordPress site.
Full site editing transforms your editing experience by integrating a range of new features that make site customization easier and more intuitive. Here are all the key components of WordPress full site editing:
- Site Editor: The Site Editor allows you to visually edit your entire website. You can change headers, footers, and everything in between directly within the editor. This unified editing experience means you no longer need to switch between the WordPress Customizer, widgets, and menus.
- Global Styles: Global Styles lets you set and manage the appearance of your site from one place. Adjust colors, typography, and spacing globally to maintain a consistent look across your site. This ensures design consistency and saves you time by applying changes across all pages and posts simultaneously.
- Templates and Template Parts: This feature lets you create, edit, and manage templates for different parts of your site. You can edit and design custom layouts for pages, posts, and other content types.
- Block Themes: Block themes are themes designed specifically for Gutenberg. They offer greater flexibility and customization options by utilizing the full power of blocks. With block themes, you can build every part using blocks, which makes it easier to create a cohesive and dynamic website.
Later in this tutorial, we will explore each of these components in detail so that you will fully understand the WordPress Gutenberg full site editing.
IMPORTANT: Make sure your WordPress site has Gutenberg enabled. If not, check out our detailed guide on how to get Gutenberg Editor in WordPress.
What’s The Objective Behind WordPress Full Site Editing?
The primary goal of WordPress full site editing (FSE) is to redefine how users build and customize their websites. FSE is designed in such a way that it lets you make changes to every element on your WordPress site by using Gutenberg blocks, not just post and page content.
This Gutenberg full site editing approach opens up numerous possibilities and benefits for WordPress users, such as:
- Editable Website Elements: With Gutenberg blocks, edit every aspect of a website, including headers, footers, and sidebars.
- Unified Design Experience: Provides uniform design across the site to maintain consistency in design without switching between different tools.
- Simplified Customization: Users can make changes visually without any knowledge of how to code.
- Visual Interface: To design a website intuitively by moving and editing blocks with a visual drag-and-drop interface.
- Dynamic Design Options: Create layouts with dynamic and flexible design options that fit your needs.
- Non-Developer Friendly: Allows non-developers to create content and design their site regardless of their technical abilities.
- Streamlined Theme Development: Theme developers can create more adaptable and user-friendly themes by optimizing theme development and customization.
- Global Style Adjustments: Improve the look and feel of the website with global style adjustments, such as changing colors, fonts, and other styles site-wide from one location.
Now, let’s explore each component of WordPress Gutenberg full site editing.
1. Site Editor
What is WordPress Site Editor?
The WordPress Site Editor is a powerful tool within the Gutenberg full site editing framework. It allows users to customize every aspect of their website using a visual, block-based interface.
Here is a quick breakdown of what you can do with the WordPress site editor:
- Full Site Customization: You can edit headers, footers, and all other areas of your site.
- Block-Based Editing: Utilizes the block layout for all parts of your website, offering a consistent editing experience.
- Access and Activation: Available when you activate a block theme from the WordPress theme directory.
- Navigation and Styles: Easy navigation through menus and direct access to edit site styles.
- Content Management: Edit the content of your pages directly within the Site Editor.
- Templates Management: Manage different layouts for various sections of your site.
- Patterns Management: Handle synced patterns and template parts efficiently.
NOTE: To use the Site Editor, you must have a block theme installed and activated on your WordPress site.
Overview of WordPress Site Editor
The Site Editor offers a new and convenient way to customize your WordPress site. It differs from the traditional page and post editors by providing a comprehensive set of tools to manage your entire site’s design.
Inside the WordPress site editor, there are three main parts:
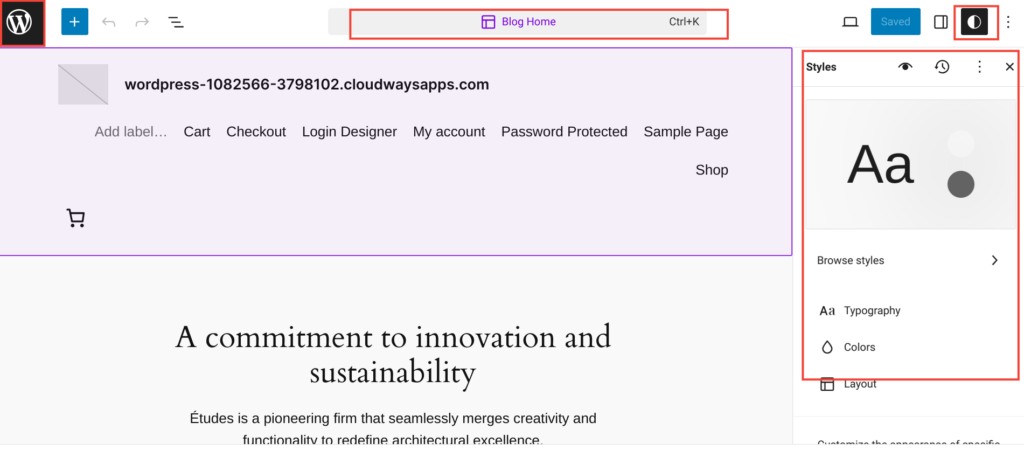
- Header: This header label shows the name of the current template you are editing. It helps you keep track of which part of your site you are working on.
- Global Styles: The new global styles option allows you to set and manage the appearance of your site from one place. You can adjust colors, typography, and other design elements site-wide, ensuring a consistent look and feel.
- ‘W’ Icon to Open Navigation: The Site Editor includes a quick navigable menu. This menu lets you switch between different templates and template parts easily. You can quickly make changes to headers, footers, and other components.
How to Find the WordPress Site Editor?
To access full site editing, first, make sure your WordPress version is updated to the latest version, at least 5.9 or newer (ideally 6.4). Also, activate a compatible theme like Twenty Twenty-Four.
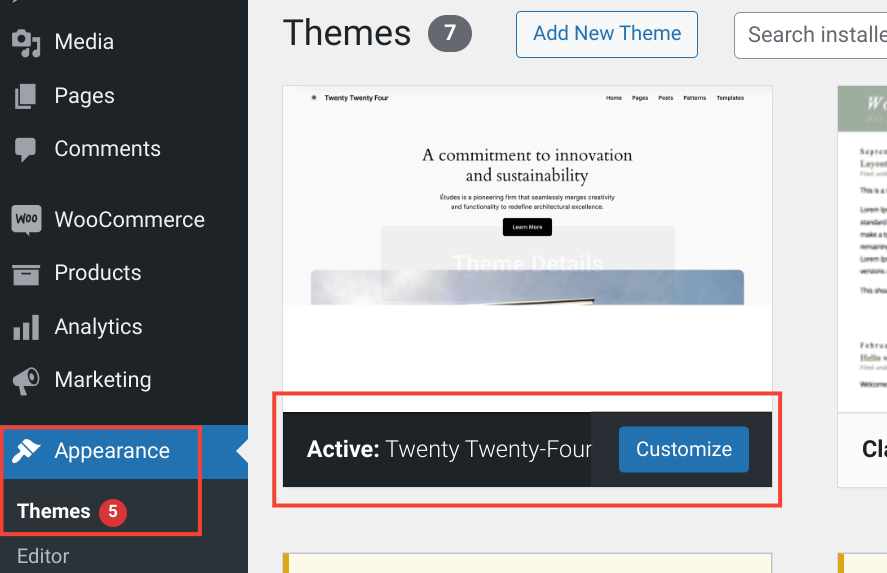
Once you have set this up, you will see a new menu item called “Editor” in the WordPress dashboard.
To get access to the WordPress Site Editor:
- Go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Click on Appearance.
- Select Editor.
This menu will take you directly to the Site Editor. Here, you can start building and customizing your entire website using the intuitive Gutenberg blocks.

2. Global Styles
Global Styles in Gutenberg full site editing (FSE) allows you to customize your site’s appearance globally. It offers a convenient interface to adjust colors, typography, and other design elements consistently across your entire site.
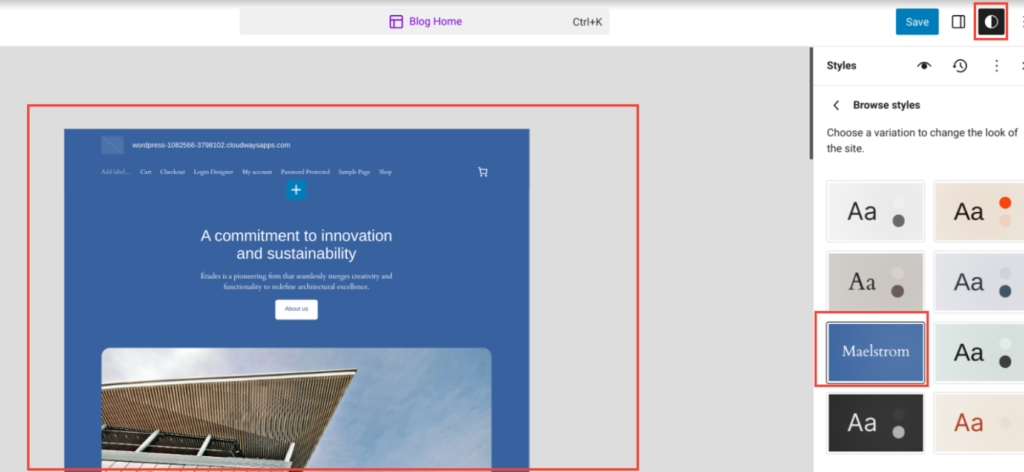
What Global Styles Are in Gutenberg Full Site Editing
When taking a high-level view, you can see that the new Global Styles feature has six categories (at the time of this Gutenberg FSE tutorial):
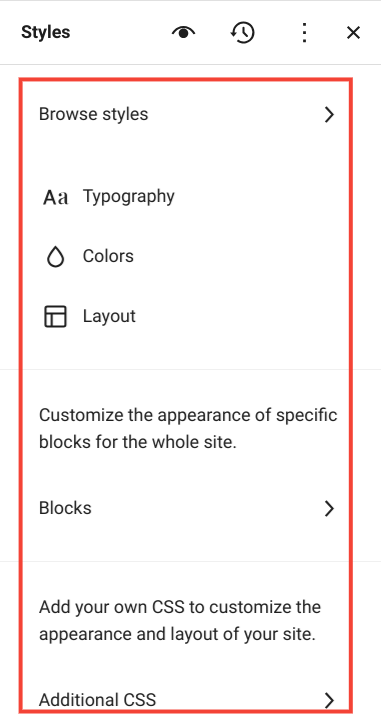
- Browse Styles
- Typography
- Colors
- Layout
- Blocks
- Additional CSS
Now, let’s explain each of them in detail.
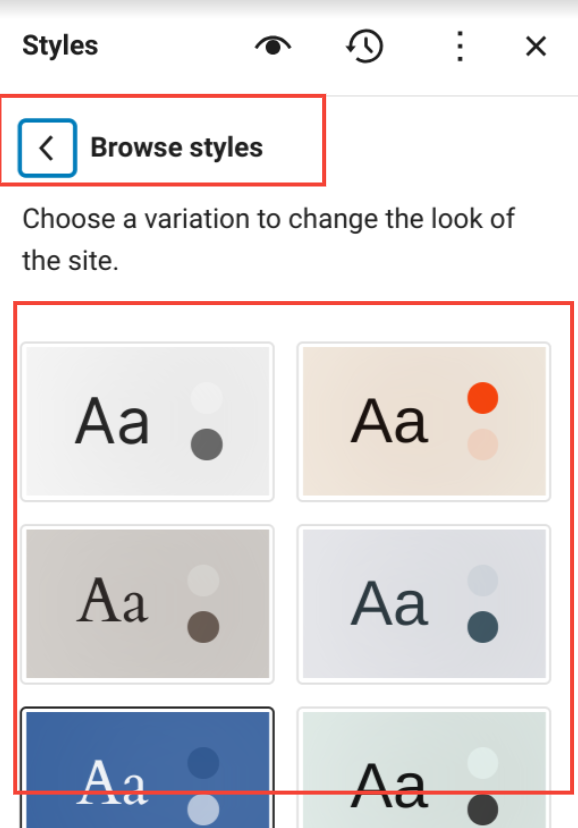
1. Browse Styles
Browse Styles in the Global Styles option of Gutenberg Full Site Editing allows users to preview and select different style variations from the pre-collected styles from the block theme for your site.
Once you select a style from the menu, you can see its effect on the left in real time.
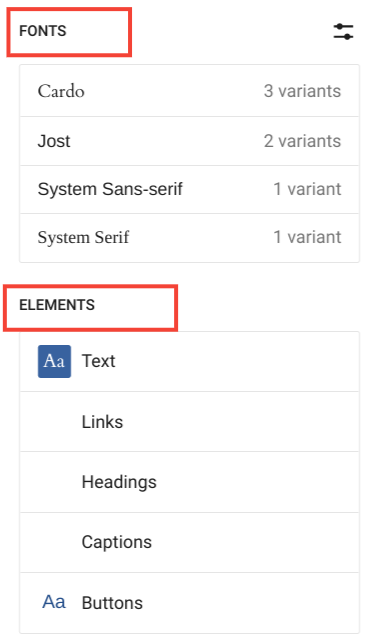
2. Typography
Typography lets you change the font of any element of your entire site. Currently, you can change the font for five elements, such as:
- Text
- Links
- Headings
- Captions
- Buttons
3. Colors
As the name suggests, you can choose the color palette for your WordPress theme and also certain elements such as Text, Background, Link, Captions, etc.
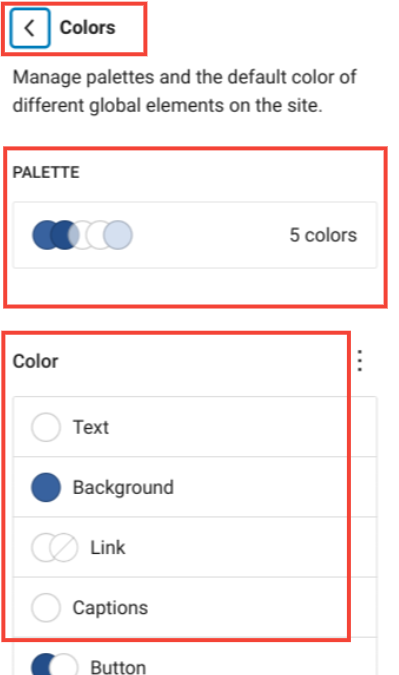
Currently, there are two subdivisions of the color section.
- Palette: With this section, you can customize the color palettes used across your WordPress site.
- Elements:
- Text: To change the color of your site’s text
- Background: You can customize the color of the site’s background
- Link: You can customize the color of links on your site.
- Captions: You can customize the color of the captions for images
- Button: You can change the color of any button on the page
- Heading: Select a different color for the heading
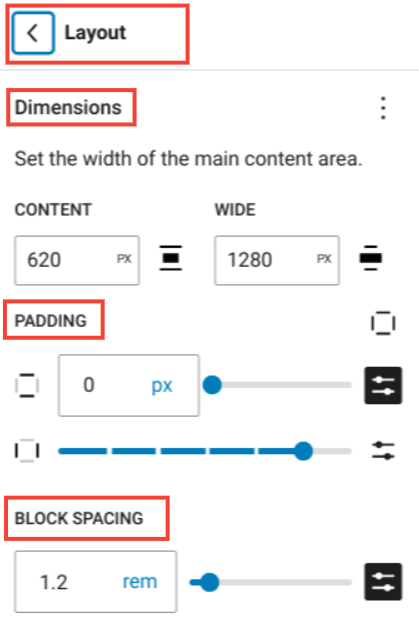
4. Layout
In this global styles section, you can customize the layout of your site, such as;
- Dimensions: Change the width and height of various site elements to achieve your desired layout.
- Padding: Adjust the internal space within element borders to create the right amount of spacing inside.
- Block Spacing: Manage the space between blocks to maintain a tidy and organized look.
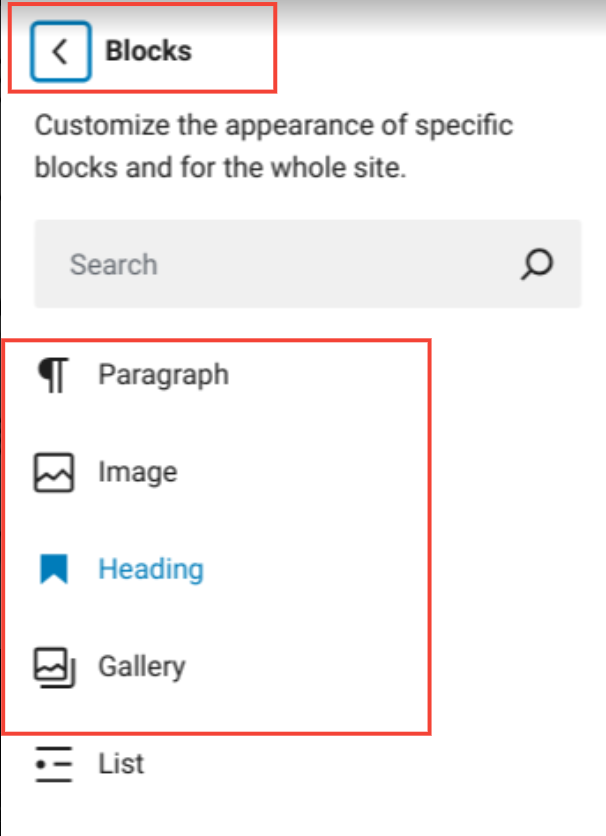
5. Blocks
In the Global Styles section, the Blocks option lets you customize the design of a particular block or block type, such as;
- Paragraph
- Image
- Heading
- Gallery
- List
- List item
- Quote, etc.
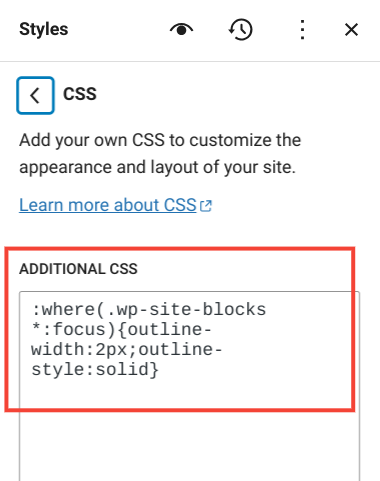
6. Additional CSS
If you want to apply custom CSS styles to customize the appearance and layout of your site, you can use this section to add the custom CSS code.
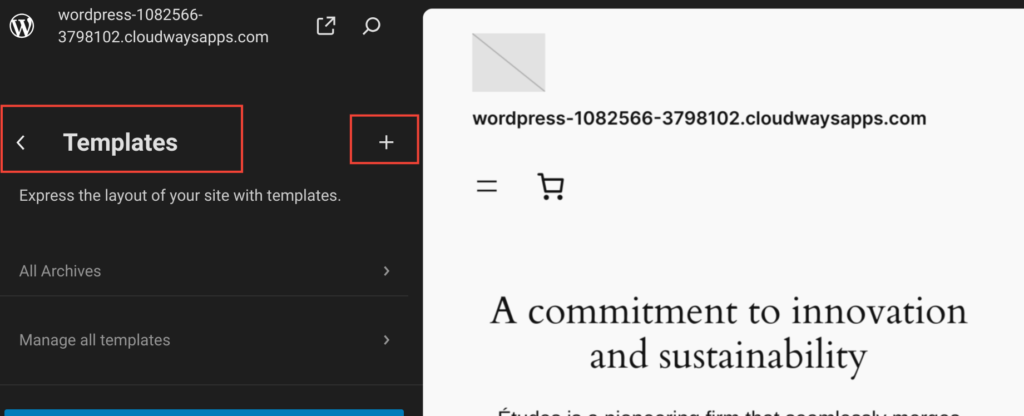
3. Site Templates and Template Parts
Templates and Template Parts in WordPress Gutenberg Full Site Editing define the structure and design of your website. They allow you to create, edit, and customize various sections of your site with ease.
- Templates: Templates are the overarching layouts for pages, posts, archives, and other content types. With templates, you can ensure that each type of content has a consistent and unique design. For example, you can create a custom template for your homepage, another for blog posts, and another for category archives.
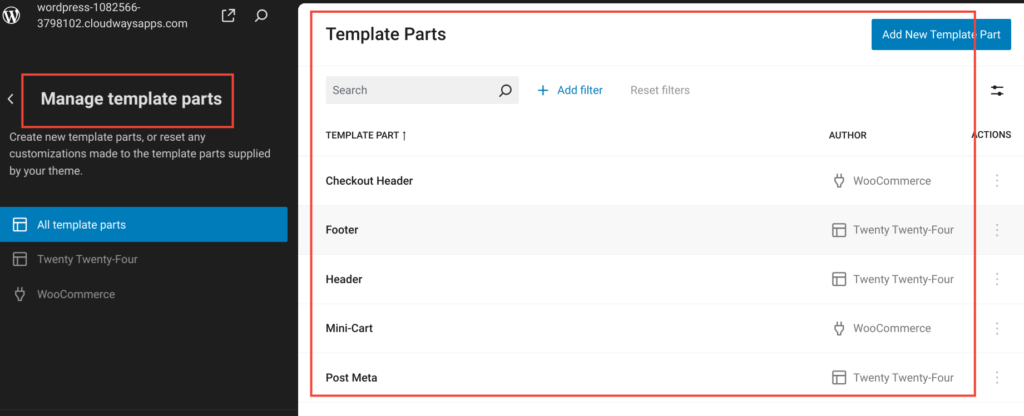
- Template Parts: Template parts are reusable sections of a template, such as headers, footers, or sidebars. By creating template parts, you can easily apply consistent design elements across multiple templates. This modular approach simplifies the process of making site-wide design changes. For instance, if you update the footer template part, the change will reflect across all templates that use that footer.
4. Block Themes
A Block theme is basically a WordPress theme that uses blocks for every part of the website, including navigation menus, headers, content areas, and footers. With these themes, you can edit and customize all aspects of your website.
Essentially, block themes represent a new approach to creating WordPress themes. They offer a more convenient, organized, and stable way to build and manage sites compared to traditional themes.
In short, block themes primarily consist of blocks that can be used throughout the site, not just within the post content, header, and footer.
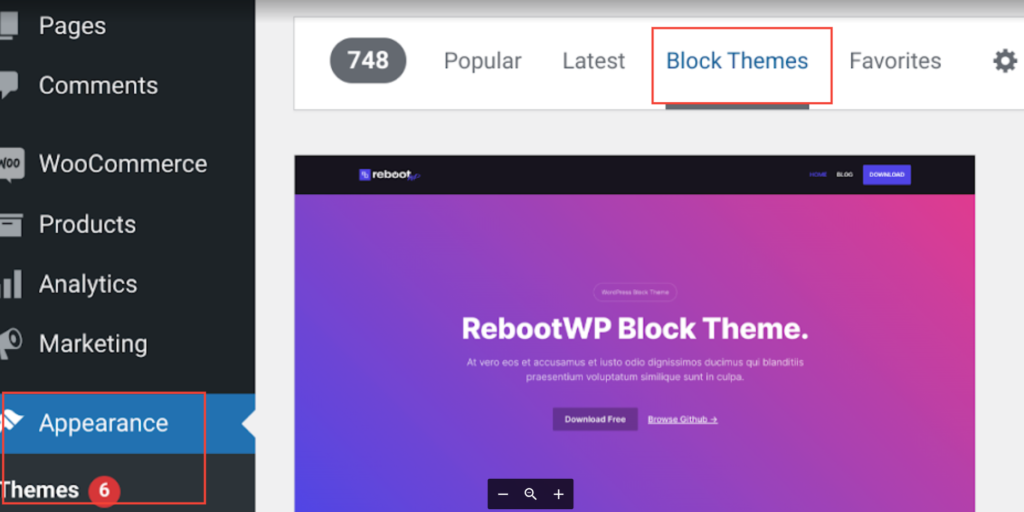
To access block themes, simply navigate to the Appearance → Themes → Add New Theme and then select Block Themes tab.
Wrapping Up
WordPress Gutenberg Full Site Editing represents a significant leap forward in website customization and design, giving users unprecedented flexibility and control.
By leveraging Gutenberg blocks for every aspect of your site, you can create a cohesive and visually appealing website without needing extensive coding skills.
From the Site Editor to Global Styles, Templates, and Block Themes, this comprehensive tutorial has covered all the essential components to help you master Gutenberg Full Site Editing.
If you have any questions, let us know in the comment section below. We would love to answer!

![WordPress Gutenberg Full Site Editing: In-Depth Tutorial [2024] WordPress Gutenberg Full Site Editing Tutorial](https://wpdesc.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/wordpress-gutenberg-full-site-editing-tutorial-1024x520.png)
![Contact Form 7 Formatting in WordPress [How to Do it The Right Way] Contact Form 7 Formatting in WordPress [How to Do it The Right Way]](https://wpdesc.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Contact-Form-7-Formatting-in-WordPress-1024x512.png)
![How to Redirect Contact Form 7 to Thank You Page [2 Easy Ways] How to Redirect Contact Form 7 to Thank You Page [2 Easy Ways]](https://wpdesc.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/how-to-redirect-contact-form-7-to-thank-you-page-1024x512.png)
![How to Add reCAPTCHA to Contact Form 7 [2 Easy Steps] How to Add reCAPTCHA to Contact Form 7 [2 Easy Steps]](https://wpdesc.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/how-to-add-recaptcha-to-contact-form-7-1024x512.png)

Leave a Reply